Front, Rear or All Wheel - What Drive is Your Car?
Modified On Oct 15, 2014 04:37 PM By Firdaus
- 1 Comments
- Write a comment
When a new car is launched car manufacturers often stress on the point that their vehicle is a front when drive, a rear wheel drive or an all wheel drive. You’ll also hear petrolheads boast of the fact that their vehicle is a rear wheel drive or RWD and how much fun it is to drift in them. But what do these terms mean, how do they affect the performance of a car and why are some of them popular among auto enthusiasts. We at CarDekho simplify this for you.
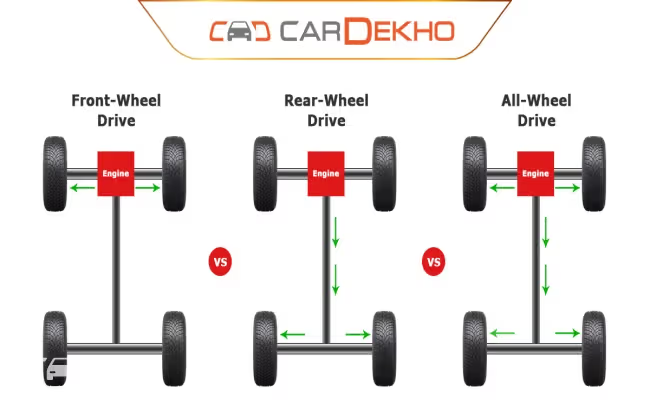
Front wheel drive aka FWD
Front wheel drive is referred to a vehicle whose front wheels are driven by the power provided from the engine. This is the most popular layout for modern cars as it is a compact arrangement in which both the engine and the driven wheels are on the same side of the car. There are two types of FWDs
1.FF- Front engine, front wheel drive
In this layout the engine is mounted in front of the axle and the two front wheels are driven by the engine power. There is no need for a propeller shaft to transfer power to the wheel; making this arrangement a popular choice for most passenger cars as it eliminates cost and helps is making the car more compact. Since most of the weight of the car is placed at the front, a FWD car is more stable in wet and snow driving conditions due to the traction that the wheels get.
Example: Hyundai i10, Skoda Rapid
2.FR – Front engine, rear wheel drive
In this layout though the engine is mounted at the front, it is the rear wheels that are driven by the engine power. The power is transferred from the engine to the rear wheels via a driveshaft. This layout is popular in racing cars as heavy acceleration pushes the weight of the car at the rear wheels giving them more traction. Since RWD vehicles need an added component to drive the power, they tend to be a little expensive than FWD cars.
Example: Toyota Innova
The brownie point for FWD cars is that since they are simpler to make and are light in weight, they deliver better fuel economy.
Rear Wheel Drive aka RWD
As the name suggests it is the rear wheels that drive the car. The power from the engine is transmitted to the rear wheels via a drive shaft. Rear wheel drive cars offer better balance and handling. In case of hard acceleration the weight is shifted to the rear wheels providing better traction. Since the drive shaft tunnel needs to be accommodated to transfer power from the engine to the rear wheels, RWD cars may sometimes compromise on interior space. Most sports cars and all race cars are rear wheel driven.
Rear wheel drive cars may have the following layouts
1.FR – Front engine, rear wheel driven. Eg – BMW 3 series
2.RR – Rear engine, rear wheel driven. Eg – Ferrari, Lamborghini, Porsche and the Tata Nano
3.MR – Mid engine, rear wheel driven. Eg – Porsche Boxter
Brownie points for RWD cars? Good handling, weight distribution and fun to drive character.
All Wheel Drive aka AWD
In an all wheel drive car the engine is mounted at the front with the power being distributed equally to all the four wheels offering better traction. AWD systems are mainly seen on sport utility vehicles and they offer better handling and traction on any kind of terrain. Some passenger cars or sports cars also sport an AWD system. Cars/ SUVs with an AWD system have a “Go anywhere” character and often favoured by off-road sporting enthusiasts.
While AWD refers to the power being delivered to all four wheels all the time, there is also a term called as 4x4. In this case as well the power is delivered to all four wheels, but the driver also has an option of switching to 2x2 mode where the power is delivered to only two wheels via the differential.
The biggest detractor for AWD and 4x4 vehicles is that they are expensive and heavy. Since making these cars involves more components, they are a tad bit expensive to maintain when compared to FWD or RWD cars.
Brownie points – All wheel drive vehicles are designed to tackle all kinds of terrain, be it tarmac or wet slushy paths, their superior handling and power delivery puts these cars in a class of their own.
Example:
AWD – Nissan GTR
4x4 – Mahindra Thar, G- Wagen
Hope this article has helped you understand the basic difference between the different drive types that come on cars. Happy revving.
2 out of 2 found this helpful










